Joëlle Moïse, Stellios Arseniyadis,* and Janine Cossy*
Laboratoire de Chimie Organique, ESPCI, CNRS, 10 rue Vauquelin, F-75231 Paris Cedex 05, France
There are two papers being published online this week in
Org Lett ASAP on exactly the same topic. The first one is from prof. Janine Cossy's group on their work studying cross metathesis (CM) between alpha-methylene-gamma-lactone. The other one will follow this post.

Several Grubbs' catalysts (all three below) were investigated, but not the Schrock's catalyst.
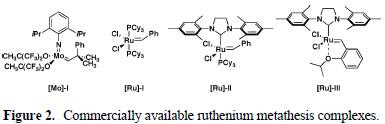
In the initial study, parent gamma-lactone 4 was subjected to reaction with alkene 5a in refluxing CD2Cl2 to prevent loss of compounds due to their volatility, and the results of which could be monitored directly by NMR. The results are summarized in the Table 1.

It was found that [Ru]-I and III did not provide any conversion while [Ru]-II produced some desired CM product 6a along with alkene isomerization product 7 in variable amounts via a well-documented mode of Ru-catalyzed reaction of alkene. It is well known that through chelation of substrate and ruthenium carbene, CM process could be shut down due to the formation of unreactive catalyst species.
In order to prevent formation of 7 and increase conversion of 4, several additives were studied, the results of which are included in Table 2.

Several points could be made from the table. Cy2PCl and Ph2PCl gave opposite results in term of ratio of 6a and 7 (entries 2 and 6). The best additive for substrate 4 was 2,6-dichlorobenzoquinone (entry 7) which entirely suppressed formation of 7 although conversion of 4 was incomplete. The other drawback of this benzoquinone additive was its inconsisitent performance, ie. it seemed to be substrate-dependent.
In addition to the benzoquinone additive, chlorocatecholborane produced quite satisfactory result. Besides, it performed more consistently with other substrates. Therefore, this catecholborane was used to investigate the scope of the reaction of lactone 4 with various alkenes as summarized in Table 3.

 All CM products could be produced in moderate to excellent yields while formations of isomerized products were largely suppressed. All cross products were formed in favor of E stereochemistry. As seen in table, in some cases, namely olefins 5c, 5h, and 5k-m conversion with 2.5 mol % of [Ru]-II catalyst and 5.0 mol % of chlorocatecholborane (the general protocol) remained low. As a result, the procedure for these olefins were modified to be the successive treatments of [Ru]-II (2 x 2.5 mol %) separated by a 7 h period.
All CM products could be produced in moderate to excellent yields while formations of isomerized products were largely suppressed. All cross products were formed in favor of E stereochemistry. As seen in table, in some cases, namely olefins 5c, 5h, and 5k-m conversion with 2.5 mol % of [Ru]-II catalyst and 5.0 mol % of chlorocatecholborane (the general protocol) remained low. As a result, the procedure for these olefins were modified to be the successive treatments of [Ru]-II (2 x 2.5 mol %) separated by a 7 h period.







No comments:
Post a Comment